
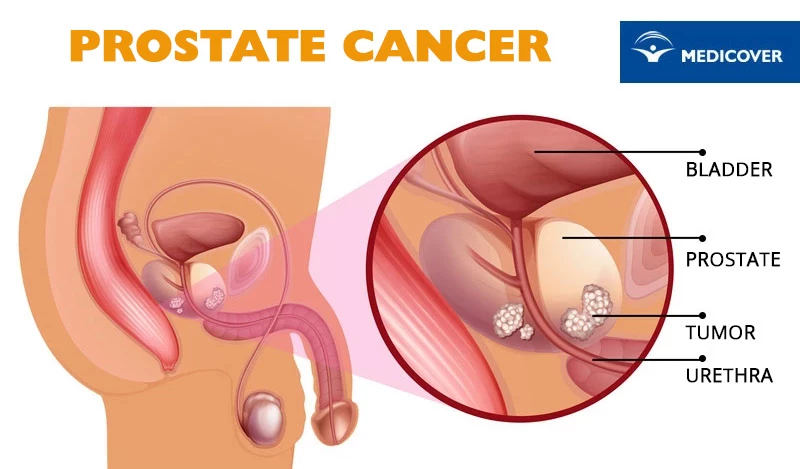
What is prostate cancer?
Prostate cancer is the most common malignant tumor in men in Poland and the second leading cause of cancer-related mortality. Every year, it is detected in about 17,000 people. patients, and more than 5,000 die because of it. men. Most cases occur between the ages of 60 and 79.
Approximately 17,000 patients in Poland are diagnosed with prostate cancer. men per year.
Symptoms of prostate cancer
Usually, prostate cancer in the early stages of the disease does not cause any symptoms or they are mildly severe. They are mainly associated with an enlarged tumor that presses on the urethra.
Early symptoms of prostate cancer:
- frequent urination,
- the need to interrupt sleep to urinate,
- an uncontrollable urge to urinate urgently,
- a feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder,
- urinating in a narrow stream,
- pain or burning when urinating
As the tumor grows, urine may remain in the bladder.
Advanced prostate cancer symptoms:
In advanced stages of the disease, symptoms may appear due to the presence of metastases. The most frequently reported complaints are:
- pain in the lumbosacral spine,
- bone pains,
- blood in semen,
- blood in the urine,
- painful ejaculation,
- abdominal pain,
- constipation
- unilateral swelling of the lower limb,
- loss of appetite,
- unexplained weight loss,
- shortness of breath
- anemia.
Prostate cancer metastases
Metastasis occurs when cancer cells spread to other organs through the lymphatic system or bloodstream. Most often, the cancer metastasizes to the bones. Less often to the liver, lymph nodes, brain and lungs. In a few cases, they are also observed in other organs (including adrenal glands, large intestine, pancreas).
Diagnosis of prostate cancer
PSA test
The prostate gland produces a protein called prostate specific antigen (PSA). The prostate antigen is responsible for keeping semen in liquid form. In addition, it is also a good indicator of prostate health.
PSA measurement is the basic test for the initial screening of the prostate gland. Most patients have an elevated blood antigen level, although elevated PSA levels are also seen in other prostate conditions, such as benign prostatic hyperplasia. In some cases of prostate cancer, no elevated PSA levels are noted.
PSA is present in serum in free and bound form. Total PSA is the sum of both fractions. Total PSA is measured first. If the obtained result deviates from the reference values in a given age group, you should contact a specialist who, if necessary, will order a free PSA test.
Rectal examination
An equally important component of the initial diagnosis is the rectal examination, which can be performed by the doctor during the physical examination. The test consists in evaluating the prostate gland with a finger through the anus. The doctor can then assess the size, consistency, and soreness of the prostate.
Your doctor assesses your risk of prostate cancer based on a number of factors, including:
- PSA antigen concentration,
- rectal examination result,
- information about illnesses in the family.
Biopsy
The diagnostic test that determines the detection of prostate cancer is the collection of samples from the prostate using a transrectal biopsy. Thanks to ultrasound, it is possible to precisely select the place where the sample should be taken for microscopic evaluation.
Other tests to diagnose prostate cancer
Computed tomography of the pelvis and abdomen and bone scintigraphy are most commonly performed to check for metastases.
Bone scintography shows changes in the skeletal system.
The basis for the diagnosis of the disease is a microscopic examination, palpation of the prostate gland and imaging tests (transrectal ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging).
Check out Medicover's offer in the field of prostate cancer screening >>
Treatment of prostate cancer
Depending on the stage of advancement, general condition and age of the patient, the doctor selects the appropriate procedure in consultation with the patient. In young men, due to the worse prognosis, more aggressive treatment is conducted.
Treatment methods
- surgical treatment - prostatectomy,
- radiotherapy,
- hormone therapy,
- chemotherapy.
Surgical treatment
Surgery to remove the prostate is mainly performed in patients with an estimated survival time of more than 10 years and no distant metastases. This procedure can be performed classically or using minimally invasive endoscopic methods, such as laparoscopy or the da Vinci robot.
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is usually used as a radical treatment alternative to surgery or as a supplement to surgical treatment. It can be divided into external and internal (brachytherapy). The prostate gland, seminal vesicles and, in the case of metastases, the surrounding lymph nodes may be irradiated.
Hormonal treatment
When the disease is already advanced and surgery or radiotherapy is not possible, hormone therapy is used. It is the most popular method of pharmacological treatment of this cancer. It can be used before surgery to increase its effectiveness or as part of palliative treatment. It consists in blocking the action of male sex hormones, which stimulate cancer cells to grow.
This effect can be obtained in two ways - by removing the testicles (historical method) or by using drugs that inhibit the hormonal axis: pituitary gland-testes. However, over time, cancer can become resistant to hormone therapy. In such cases, pharmacological treatment may sometimes be supplemented with chemotherapy.
In selected cases, no treatment methods are used, but only close observation and health control is carried out. Treatment is only started when the disease has progressed in follow-up examinations. This method does not adversely affect the prognosis if used in the right group of patients, i.e. in men with low-grade prostate cancer.
Check out Medicover's prostate cancer treatment offer >>
Risk factors and causes of prostate cancer
The risk of developing prostate cancer increases with age. Most cases are diagnosed in patients over 60 years of age. This cancer is very rarely detected in young men.
It has been proven that genetic factors play an important role in the development of prostate cancer. If one of the family members (father, brother) was sick, the risk of getting sick is twice as high. If there were more patients in the family, the risk increased 9-11 times.
Men who have a family history of the BRCA gene mutation, which is responsible for an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer in women, are also more predisposed to the disease. Family history of the disease is an indication for genetic tests for the development of this cancer.
In addition, obesity and an unhealthy lifestyle also play an important role in the development of prostate cancer. Consuming excessive amounts of red meat, milk and processed grain products may increase the risk of developing this cancer.
Prognosis and complications of prostate cancer
The prognosis of prostate cancer depends on the stage of the disease and the general condition of the patient.
The most common complications of prostate cancer treatment include:
- erectile dysfunction,
- incontinence,
- hematuria,
- rectal bleeding
- decreased libido,
- gynecomastia.
Prevention of prostate cancer
Men over 50 years of age without a family history of prostate cancer should have their PSA level measured once every 1-2 years with or without palpation of the prostate gland.
Conversely, men with a family history of prostate cancer in a first-degree relative should start PSA testing as early as age 40 or 45 with or without digital rectal examination. Depending on the result obtained and individual risk, this parameter should be determined once every 1 or 2 years.
Such a procedure will enable the detection of possible changes at an early stage and prompt initiation of appropriately selected treatment. Nutrition is also important in the prevention of prostate cancer. Eating enough vegetables and fruits, as well as fatty sea fish, can reduce the risk of disease. It is especially recommended to follow the principles of the Mediterranean diet, which provides valuable vitamins and minerals, phytochemicals, omega-3 fatty acids and dietary fibre.
Medicover offer
|
The presented medical information should not be treated as guidelines for medical conduct in relation to each patient. The medical procedure, including the scope and frequency of diagnostic tests and/or therapeutic procedures, is decided by the doctor individually, in accordance with medical indications, which he determines after getting acquainted with the patient's condition. The doctor makes the decision in consultation with the patient. If the patient wants to perform tests not covered by medical indications, the patient has the option of paying for them. |
Prezentowanych informacji o charakterze medycznym nie należy traktować jako wytycznych postępowania medycznego w stosunku do każdego pacjenta. O postępowaniu medycznym, w tym o zakresie i częstotliwości badań diagnostycznych i/lub procedur terapeutycznych decyduje lekarz indywidualnie, zgodnie ze wskazaniami medycznymi, które ustala po zapoznaniu się ze stanem pacjenta. Lekarz podejmuje decyzję w porozumieniu z pacjentem. W przypadku chęci realizacji badań nieobjętych wskazaniami lekarskimi, pacjent ma możliwość ich odpłatnego wykonania. Należy potwierdzić przy zakupie badania szczegóły do jego przygotowania. |
