Cancer is a growing health problem in Polish society. According to the report of the National Cancer Registry, over 171,000 cancers are reported annually. new cancer cases and over 100,000 deaths. In Poland, malignant neoplasms are the second cause of death, accounting for 25.7% of male deaths and 23.2% of female deaths. Prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, followed by lung cancer and colorectal cancer. Women are more likely to suffer from breast cancer, followed by lung cancer and colorectal cancer.

Table of Contents:
- What is prevention?
- What are the risk factors for developing cancer?
- 12 rules of cancer prevention
- Medicover Prevention Standard
According to experts, prevention plays the most important role in preventing cancer. It is thanks to it that we can reverse the unfavorable epidemiological trends in this area.
What is prevention?
Health prevention is planned activities. They are used to maintain the best possible level of health and early recognition of health threats - i.e. health risks, to support a healthy lifestyle, to detect diseases at their early stage and to support the treatment process through education.
The World Health Organization distinguishes three phases of prevention:
- Primary (early) prevention prevents disease by establishing healthy lifestyle patterns and controlling risk factors. It is used to reduce the incidence of disease by reducing the risk of developing the disease. The basic methods of primary cancer prevention include: dissemination of knowledge about oncology, promotion of the so-called oncological vigilance and promoting healthy behaviors and a healthy lifestyle.
- Secondary prevention consists in preventing the consequences of the disease thanks to its early detection and treatment (screening test).
- Tertiary prevention (metaprophylaxis) concerns inhibiting the progression of the disease and limiting complications.
What are the risk factors for developing cancer?
Cancer is an abnormal tissue that results from the uncontrolled growth of certain cells in the body. It is a genetic disease caused by changes (mutations) in DNA (genes) resulting from the process of carcinogenesis. There can be many reasons for this situation, but they have been classified into two categories. Risk factors, i.e. all conditions that increase the chance of developing cancer, are divided into:
- modifiable factors – those we can influence, eg smoking, poor diet, excessive body weight, exposure to carcinogens;
- non-modifiable factors – independent of us, not subject to change, eg age, gender, genetic predisposition.
According to the current state of knowledge, even 70-90% of cancers are determined by external environmental factors that we have a real influence on. A small part of cancers develops as a result of inheriting specific predispositions. Hereditary factors are associated with about 10-30% of cases.

Cancer and genetic predisposition
Cancer itself is not inherited, i.e. passed from parents to children, but a genetic change that increases the risk of developing cancer can be inherited. Some types of cancer, mainly breast, ovarian, colorectal and prostate cancer, are strongly linked to genes and may run in families. Therefore, it is important to know your family's medical history, especially the incidence of cancer. Inheriting a genetic change associated with cancer does not mean that you will definitely develop the disease. It only means that the risk of developing cancer is increased. Through molecular and genetic diagnostics, it is possible to exclude or determine the carrier of a gene mutation among family members and to provide them with proper care in genetic clinics. Awareness of the load in the genes allows you to take appropriate preventive measures and motivates you to regular screening tests, which enable early detection of neoplastic changes.
You can read more about it here: DNA-BASED RESEARCH
12 rules of cancer prevention
Although most cancers are diagnosed in middle-aged and elderly people, the vast majority of them are the result of long-term accumulation of DNA damage resulting from our health behaviors. The first changes in cells can appear much earlier - already in youth. Therefore, by following the simple rules of a healthy lifestyle, we are able to significantly reduce the risk of cancer. According to the estimates of the World Health Organization (WHO), up to 50% of all cancer cases can be avoided by promoting and introducing healthy habits in societies.
A set of valuable tips and preventive recommendations in this area has been defined in the European Code Against Cancer, a document that was created over 35 years ago. The European Code Against Cancer (The EuropeanCodeAgainstCancer) was inspired by the European Commission. It aims to educate the public about the actions that are worth taking to reduce the risk of developing cancer. It consists of twelve recommendations that most people can follow without any special skills.
1. Do not smoke. Do not use tobacco in any form.
Tobacco smoking is the cause of many diseases and premature death in developed countries. It causes, among others: laryngeal and lung cancer, oral cavity cancer, ovarian cancer, pancreatic cancer, kidney cancer and myeloid leukemia. Cigarette smoking also increases the risk of intestinal polyps by 2-3 times from which cancer may develop. Numerous studies have shown that smoking more than 20 cigarettes a day for 35 years increases the risk of developing colorectal cancer by 50%.
Smoking is responsible for 82% of all lung cancer cases and one third of all cancer cases. Regardless of whether we take tobacco in the form of cigarettes or cigars, whether cigarettes are filtered or unfiltered, strong or light - tobacco remains invariably carcinogenic. The same applies to currently fashionable e-cigarettes. Due to the nicotine content, electronic cigarettes are as addictive as traditional cigarettes and expose the body to identical harmful substances, such as arsenic.
Tobacco smoke contains over 4,000 chemicals. Of these, at least 250 are harmful and at least 60 cause cancer.
The risk of developing lung cancer depends primarily on the duration of the addiction and the number of cigarettes smoked. Smoking 1 to 4 cigarettes a day increases the risk of lung cancer 3 times in men and 5 times in women. Long-term smokers die at a younger age - half live 20-25 years less than non-smokers.
In 2019, 21% of Poles admitted to heavy (daily) smoking. Addiction is more common in men than women: 26% vs. 19%.
Cessation of smoking is therefore the most effective method of reducing the risk of developing several cancers. Research shows that quitting smoking at any age has health benefits. If this happens before the age of 40, the risk of diseases caused by smoking is reduced by about 90%. Quitting smoking completely, even at the age of 50 or 60, can extend your life by 6 and 3 years, respectively.
Check your motivation to quit smoking: https://tiny.pl/wjtbm

You can find more about addiction here
If you want to quit smoking and need help, contact a doctor, psychologist or call the National Telephone Help Center for Smokers (tel. 801-108-108 or 22 211 80 15), run by the Oncology Center - Institute in Warsaw. The clinic is open from Monday to Friday from 11.00 to 19.00. There you will receive support and information about the nearest facility implementing a treatment program for smokers. |
2. Create a smoke-free environment at home. Limit passive smoking.
Not only smokers are exposed to the harmful effects of cigarette smoke, inhaling the so-called main smoke, but also people nearby inhaling side smoke. In such cases, we are talking about passive smoking, i.e. inhalation of tobacco smoke from the so-called second hand smoking. This situation also occurs in the case of smoke from a smoldering cigarette. Sidestream cigarette smoke contains three to four times more toxins than mainstream smoke.
Passive smoking increases the risk of cancer many times over. It is also the cause of many other diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases (heart attacks, strokes, coronary heart disease) and respiratory diseases (e.g. chronic obstructive pulmonary disease). It also contributes to the exacerbation of existing diseases, such as asthma.
Due to forced passive smoking, there are about 600,000 premature deaths annually in the world, of which 31% are children and as much as 64% are women. In Poland, about 2,000 people die who have never smoked themselves.
In 2010, an amendment to the Act on health protection against the consequences of using tobacco and tobacco products was introduced in Poland. The provisions introduced there prohibit smoking in public places and in workplaces. However, according to research, over 14 million Poles are exposed to passive inhalation of tobacco smoke at home, and over 4 million in the workplace.

It is worth expanding smoke-free zones. In addition to legally regulated non-smoking places, create places where smoking is prohibited: make sure not to smoke at home, on the balcony, staircase or in the car.
3. Maintain a healthy weight.
Obesity is a documented cause of cancer morbidity and mortality. It is the second most important cancer risk factor after smoking. This is due to the affinity of some cancers to the level of hormones, e.g. estrogen, in the body. Obesity - especially abdominal - causes additional, abnormal release of hormones from adipose tissue cells, which may accelerate or even initiate the development of cancer. Excess fat in the body also causes greater resistance to insulin and intensifies inflammatory processes that can lead to DNA damage, and thus create conditions for the formation of cancer.
The risk of developing cancer increases in proportion to the amount of fat in the body.
Excess body weight is a problem affecting more than half of the population and the cause of the development of many diseases. Overweight and obesity are linked to many types of cancer, such as esophageal, colorectal, gallbladder, ovarian, prostate and breast cancers. There is also an increased risk of developing leukemia, multiple myeloma and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Based on epidemiological studies that determine the relationship between BMI and cancer, it has been shown that each increase in BMI by 5 kg/m2 means a 30 to 60% increased risk of endometrial cancer, adenocarcinoma of the esophagus and kidney cancer. The likelihood of developing colorectal and pancreatic cancer also increases. Research results also suggest a relationship between abdominal obesity and endometrial cancer. The risk of developing this cancer in women with a BMI>25 is 3 times higher.
So what to do to maintain a healthy body weight:
- choose products that have few calories per 100 grams,
- eat regularly, without skipping meals,
- hydrate the body,
- be physically active,
- control your weight.
The most popular indicator for assessing body weight is BMI (Body Mass Index).

According to the WHO, overweight adults (over 19 years of age) are diagnosed with a BMI equal to or greater than 25.0 kg/m², and obese with a BMI equal to or greater than 30.0 kg/m².
Check for yourself if your weight is correct using from the BMI calculator
The second indicator that allows you to assess the type of obesity is the WHR (waist-to-hip ratio), i.e. the ratio of waist circumference to hip circumference. WHR is a supplement to BMI. Its calculation is not complicated and consists in calculating the ratio of waist circumference in cm to hip circumference.

Check your WHR using our calculator
It is also worth noting that maintaining a healthy body weight also reduces the risk of other health complications, such as heart disease or diabetes.
We invite you to listen to podcasts on obesity on the Medicover Polska Youtube channel.
4. Be physically active in your daily life. Limit the amount of time you spend sitting.
Physical activity is a proven protective factor, i.e. protecting us against cancer, e.g. colorectal cancer, breast cancer and endometrial cancer. According to experts - high physical activity during life is associated with a reduction in the incidence of certain cancers by at least 25% compared to people who are not very active.
Regular physical activity:
- Helps maintain a healthy body weight
- Reduces the risk of heart disease, some cancers and type 2 diabetes
- Stabilizes the joints and spine
- Increases disease resistance
- Has a positive effect on mental health - sport eliminates anxiety and "clears the mind"
Therefore, WHO recommends adults:
- at least 150-300 minutes of endurance (aerobic) effort of at least moderate intensity or ≥ 75-150 minutes of high-intensity or equivalent combination,
- at least 2 times a week strength training of at least moderate intensity, involving all major muscle groups.
Moderate intense physical activity
| High-intensity physical activity
|
WHO recommends doing - persons aged 18-64 for 150-300 minutes a week - persons aged >65 for 150 minutes per week While doing it, you can freely talk to the other person, you can also sweat slightly | WHO recommends performing: - people aged 18-64 for 75-150 minutes a week - people aged >65 for 75 minutes a week It requires a lot of effort Increases the respiratory rate significantly While doing it, you can only say a few words without pausing to catch your breath, it causes high sweating. |
Examples | |
|
|
It is worth remembering that the less time we spend in a sitting position, the better it is for our health. In men, sitting for more than 9 hours a day can increase the risk of colorectal cancer by up to 61%. Sedentary women, on the other hand, are at higher risk of developing ovarian and breast cancer. Therefore, if, for example, we spend a lot of time in front of the computer, it is worth getting up and moving around for at least a few minutes once an hour.
You can read about the impact of physical activity on health here

5. Follow the recommendations of proper nutrition
Proper nutrition plays an important role in the prevention of cancer. It is estimated that the cause of nearly 30% of cancers is an unhealthy diet. This is influenced by both the combination of consumed foods and their quantity, which translates into the possible occurrence of obesity - another risk factor for the development of cancer, but also the quality of products. At the moment, more than 500 food ingredients have been identified that affect the process of carcinogenesis (cancer formation).
Following a proper diet can reduce the risk of developing, among others, cancer of the esophagus, cancer of the oral cavity, pharynx and larynx, colorectal cancer, stomach cancer, breast cancer and colon cancer. A properly balanced diet is an important element of primary prevention of oncological diseases. However, the way of nutrition also significantly affects the effectiveness of therapy, the quality and length of life of a patient diagnosed with cancer, as well as the possible recurrence of the disease.
In the prevention of cancer, it is recommended to consume at least 5 portions (400-600 g) of vegetables and fruit every day, of which ¾ should be vegetables and ¼ fruit. These products provide vitamins, minerals and dietary fibre, but they are also a source of many anti-cancer substances, such as carotenoids, flavonoids, folates, isoflavones or antioxidants that fight free radicals and inhibit the process of cancer formation. It is worth eating a variety of vegetables and fruits, especially in raw form. Low-starch vegetables are especially recommended, including:
- lettuce,
- cucumbers,
- tomatoes,
- cabbage - plain and sauerkraut,
- pepper,
- onion,
- radish.
On the other hand, in the case of fruit, the most beneficial substances are found in berries, such as:
- blueberries,
- blackberries,
- raspberries,
- strawberries,
- cranberries.

Most meals should also include the least cleaned and processed cereal products, e.g. wholegrain bread, thick groats or bran, and legumes. These products are rich in dietary fibre, which reduces the energy content of meals, helping to maintain a healthy body weight, affects the functioning of the intestines and the composition of the bacterial microflora.
An essential component of the diet used in the prevention of cancer are also polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA), especially omega-3. Their sources include: rapeseed oil, linseed oil, olive oil, nuts, linseed, sunflower and pumpkin seeds, avocado, cocoa, olives and fatty sea fish. They inhibit the multiplication and dissemination of cancer cells, and also mobilize the immune system to fight them.
Some products may increase the risk of cancer. One of them is meat, especially red meat and its products, which provide a large amount of saturated fatty acids and cholesterol. Additives used during breeding, meat processing (nitrates, nitrites) or during heat treatment also have an adverse effect. Therefore, it is recommended to reduce its consumption to about 3 servings per week (350-500g).
You should also limit the consumption of highly processed products, such as sweets, pastry, sweet drinks, fast food. They are characterized by high energy content and the content of saturated fatty acids. In addition, they provide large amounts of simple carbohydrates, as well as trans fatty acids, the consumption of which can lead to the growth and multiplication of cancer cells.
A properly balanced diet, tailored to the individual needs of the body, providing vitamins, minerals and polyphenols, plays an important role in the prevention of many diseases, e.g. cancers.
The following recommendations will help you to compose your meals and improve your eating habits:


Check what a proper diet looks like?
6. Limit alcohol consumption.
Alcohol consumption is a risk factor for many types of cancer, including cancer of the mouth, throat, larynx, esophagus, liver, colon and breast. In 2016, alcohol-related cancers accounted for an estimated 400,000 deaths worldwide, mostly among men.
The products of alcohol metabolism in the body are the most harmful, i.e. acetaldehyde, which can damage the genetic material of cells (DNA) and disrupt its repair mechanisms. Drinking alcohol is the cause of many other diseases, such as cirrhosis and pancreatitis. Alcohol can also increase the levels of certain hormones, such as estrogen.
There is no safe amount of alcohol. Even the smallest amount of alcohol has carcinogenic potential. The type of alcohol consumed is not the key here. It doesn't matter if it's spirits, wine or beer. The risk of developing cancer increases with the amount of alcohol consumed. In addition, the simultaneous consumption of alcohol and smoking greatly increases the risk of m. cancers of the head and neck (especially cancer of the tongue, throat and esophagus). Completely breaking both addictions would reduce the number of cases of oral cancer by as much as 83%.
Doctors emphasize that the term "alcohol abuse" includes not only drinking large amounts of alcohol or getting drunk, but also drinking alcohol in small amounts, but on a regular basis.
While abstinence from alcohol is recommended, it can be very difficult to achieve in society. Therefore, the so-called low-risk alcohol drinking limits. Alcohol consumption should be limited to:
- Women - 1 unit (10 g alcohol/day)
- Men - 1-2 units (20g alcohol/day)
How to calculate the amount of alcohol consumed?
One unit of alcohol is:
- 250 ml of beer
- 1 glass of wine
(approx. 150 ml)
- 1 shot of vodka
(approx. 30 ml)
Alcohol - unit conversion
Read: https://www.medicover.pl/o-zdrowiu/alcoholic beverages-leczenie-i-skutki-uzalezrzenia,6178,n,192
7. Avoid excessive exposure to sunlight.
The sun puts us in a good mood, gives us energy, raises the level of hormones and facilitates the absorption of vitamins. It banishes depression, activates the thyroid gland, lowers sugar levels. However, solar radiation can also be dangerous. If we sunbathe for too long and without proper protection, it can cause allergies, skin diseases, discoloration and burns. Excessive exposure to UV radiation is also the main culprit in skin cancer, among them the most aggressive form - melanoma.
People with pale and freckled skin, fair hair and blue eyes are particularly at risk of skin melanoma, as they are most susceptible to sunburn. Some studies show that fair-skinned people are up to twice as likely to develop melanoma compared to dark-skinned people. In turn, a large number of moles and a positive family history of skin cancer increases the risk up to 4 times.
So how to use the beautiful, sunny weather wisely?

Use creams that protect against UVA and UVB rays (with SPF ≥ 30). Apply the cream about 30 minutes before going outside and then repeat the application every 2 hours. or after getting out of the water.

During the hours of the greatest sunlight, i.e. 10.00-15.00, limit your stay in the sun or try to use shaded places.

Wear hats and sunglasses with an appropriate filter.

Do not use the solarium.

Also remember to observe and control pigmented moles on the skin.
8. Protect yourself from carcinogenic substances in the workplace.
Cancer develops from a few to even several dozen years from the moment of first contact with a carcinogen. We are exposed to these factors from all sides, not only in everyday life at home or outside, but also in the professional environment. Epidemiological studies show that occupational exposure to carcinogens causes between 5.3 and 8.4 percent of all cancers worldwide. According to current knowledge, about 25 types of cancer are associated with work performed in harmful conditions. The most important cancers of this type include: lung, bladder and skin cancers, malignant cancers of the nasal cavity, sinuses and larynx, leukemia and lymphomas. The greatest damage to the body is caused by:
- dust containing silica,
- wood dust,
- exhaust gases from diesel engines,
- benzene,
- asbestos,
- fromaldehyde,
- polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons,
- compounds of chromium, cadmium, nickel,
- radon decay products.
Car mechanics, boiler manufacturers, carpenters, fitters, electricians, steelworkers, shipyard workers, construction workers and railwaymen are exposed to particular occupational risk.
Therefore, compliance with occupational health and safety regulations is the basic duty of every employee and employer. These regulations protect us against the effects of substances that are dangerous and harmful to health. It is very important that everyone who is exposed to hazardous substances at work complies with these regulations and, depending on the type of risk, uses personal protective equipment. You can't eliminate exposure to carcinogens, but you can definitely reduce their exposure in your workplace. Remember! Follow the recommendations regarding occupational health and safety.
9. Protect yourself from radon radiation at home.
Radioactive elements occur naturally in the earth's crust. One such element is radium. As it decays, it emits radon, a colorless and odorless gas that is also radioactive. Radon itself does not directly affect our body. However, its decay products combine with dust particles in the air. Radiation emitted by inhaled radon decay products can damage the respiratory epithelium and initiate the development of lung cancer. This phenomenon is intensified by simultaneous smoking of cigarettes and exposure to radon radiation.
Radon is present in every building. It enters the air from the soil through cracks in foundations or leaks in sewage pipes. A small pressure difference is responsible for the penetration of radon, which results in the formation of the so-called "chimney effect" - air from the ground on which the building stands is sucked in through the cracks in the foundations of the house.
So how do you protect yourself from radon? First of all, you need to realize that this substance cannot be eliminated from the environment. However, you can lower its concentration, among others:
- sealing gaps in foundations,
- covering the walls with paints, wallpapers,
- often airing rooms,
- using special air ventilation systems at home.
10. For women: If you can, breastfeed and limit your use of hormone replacement therapy.
In Poland, the most frequently diagnosed cancer among women is breast cancer, diagnosed in an average of 19,620 women per year. The following places among typical female cancers are: endometrial cancer (about 6,000 women), ovarian cancer (nearly 4,000 women) and cervical cancer (2,300 women).
Scientists link the reasons for the dynamic increase in the number of women with hormone-dependent cancers (listed above) to, among others: the number of pregnancies, the age of first childbirth, the first menstruation and the age of menopause.
One of the factors that has been particularly highlighted is breastfeeding. It brings many health benefits - both for the baby and for the mother. It has been noticed that breastfeeding delays the onset of menstruation after childbirth, which shortens the time of exposure to hormones from the group of estrogens, which are carcinogenic. In addition, scientists have noticed that lactation changes gene expression and allows the woman to get rid of cells with damaged DNA, which could be the beginning of cancer. It is estimated that breastfeeding for more than 12 months reduces the risk of breast cancer by 28%, and by about 4.3% each year thereafter. Importantly, this relationship has been proven both in the pre- and postmenopausal period. Breastfeeding may also reduce the mother's risk of ovarian and endometrial cancer.
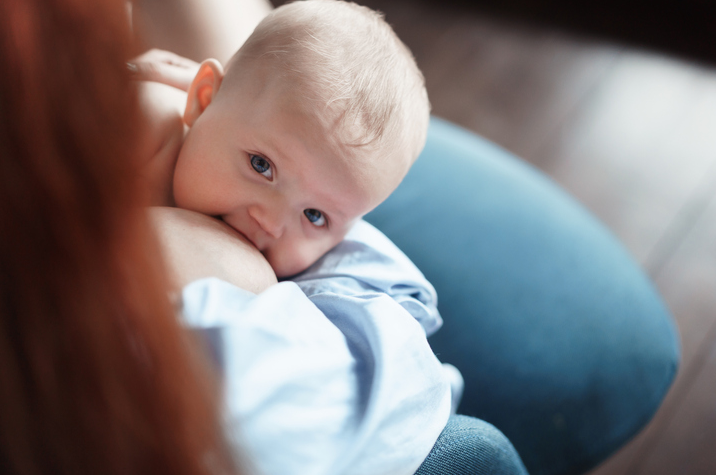

The World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months of life and continued breastfeeding until the age of two with complementary foods. As a rule, doctors promoting breast feeding of a child were paediatricians, obstetricians and family doctors, but taking into account the latest research, oncologists have also joined this group.
Another factor that may contribute to the development of cancers typically found in women, especially breast and endometrial cancer, is hormone replacement therapy (HRT). Menopausal women often decide to use HRT, which allows them to avoid or alleviate the symptoms associated with the menopausal process, such as hot flashes, sweating or vaginal dryness. Although HRT is highly effective in this application, apart from reports on its relationship with cancer, it also raises many concerns related to the long-term effects of its use, e.g. an increased risk of dementia, stroke or heart attack.
After 5 years from the end of hormone replacement therapy, the risk of developing the disease decreases and is equal to the population risk.
It is important for women to be aware of preventive measures that can protect them from the development of cancer. They can, if possible, breastfeed their child and, when using hormone therapy, regulate its duration under the supervision of qualified specialists.
11. Vaccinate children against HBV and HPV.
Few people associate chronic viral or bacterial infections with cancer, but infectious agents are responsible for 15–20% of malignancies. This applies primarily to cervical cancer, liver cancer, stomach cancer and some cancers of the blood system.
Viruses are of greatest importance in oncogenesis:
- human papilloma virus (HPV),
- hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV),
- Epstein-Barr virus (EBV),
- herpes virus 8 (HHV-8),
- human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 (HTLV-1) and type 2 (HLTV-2).
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterial agent with a potential carcinogenic effect.
Some of these infections can be prevented by vaccination. Vaccination against hepatitis B and aggressive types of human papillomavirus (HPV) are of key importance in cancer prevention.
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the HBV virus (Hepatitis B Virus). It can take an acute or chronic form. It is often asymptomatic in the first stages, which makes it particularly dangerous. HBV is an extremely insidious adversary because it is up to 100 times more infectious than HIV.
Infection can occur when:
Contact of a person with cuts on the skin or mucous membranes with secretions of an infected person (saliva, mucus, semen),
- contact with infected blood,
- sexual contact with an infected person,
- contact with contaminated, non-sterile needles and surgical instruments,
- childbirth by previously infected mothers.
Chronic infection with hepatitis B (HBV) or hepatitis C (HCV) viruses accounts for more than 2/3 of new cases of primary liver cancer in Europe. You can protect yourself against HBV infection with vaccinations that are available for all ages. Full immunization against HBV infection requires three doses of the vaccine. According to the Protective Vaccination Program (PSO), the first dose is administered to the child on the first day of life, the second dose in the second month of life, and the third dose 6 months after the first dose. The immunity acquired in this way is long-lasting.
If an HBV or HCV carrier additionally drinks a lot of alcohol or smokes cigarettes, it increases the risk of developing liver cancer. Alcohol in combination with tobacco increases the probability of developing cancer in people who stop these drugs 10 times more likely (compared to the risk in people who do not use these drugs) ).
Another dangerous microorganism for human health is the human papillomavirus HPV (Human Papillomavirus). Out of over 150 types of this virus, no more than a dozen are highly carcinogenic. In Europe, 70% of cervical cancer cases are caused by two HPV types: 16 and 18. They are responsible for cervical precancerous lesions and cervical cancer. Papilloma virus infections can also lead to anal, vaginal, vulvar or penile cancer. The milder types of HPV: 6 and 11 - cause warts on the genitals. Although they are not malignant changes, they can cause many unpleasant ailments.
Infection occurs through sexual contact, and the number of sexual partners and early sexual initiation increase the risk of infection. It is estimated that up to 80% of sexually active men and women have been or will be infected with HPV in their lifetime. According to current medical knowledge, all cases of cervical cancer are caused by chronic HPV infection. The likelihood of starting the neoplastic process after HPV infection increases in the case of smoking, weakening of the immune system or other sexually transmitted diseases.
In Poland, there are 3 types of HPV vaccinations (2-valent, 4-valent, 9-valent), recommended depending on the number of virus types from which we want to protect our body. They are recommended for girls and young women and boys and young men between the ages of 9 and 26. The vaccine prevents new HPV infections but does not cure existing infections or diseases. Therefore, it works best when given to people who have not yet engaged in sexual activity. Effective vaccination consists of three doses, usually taken in a 0-2-6 month schedule.
In our country, vaccination is currently not reimbursed, although intensive work is underway to introduce a vaccination program for teenagers. Vaccinations are voluntary, but not very popular due to the high price. Despite the financial aspects, it is worth considering providing such protection to your children, because the experience of other countries, including UK, show a 90% reduction in infection with HPV types 6, 11, 16 and 18 and a 90% reduction in genital warts.
Please note that vaccination does not exempt you from regular preventive examinations. Pap smears after vaccination are still necessary.
Vaccinations build our immunity to oncogenic viruses and give us the opportunity to protect ourselves from cancer and its effects. Preventive actions from an early age build immunity and allow you to grow up safely with a lower risk of developing cancer.
12. Use screening tests.
In addition to primary prevention, secondary prevention plays an important role. screening. It enables the detection of precancerous conditions or an early form of cancer even before the appearance of the first symptoms of the disease. It is worth realizing that an early detected cancer gives a better chance of being cured, and treatment can be carried out using methods that are more patient-friendly. Early diagnosis also reduces the risk of metastasis or recurrence, which in total extends life and improves its comfort.
Screening tests cover the population of people most likely to develop a particular cancer. Thanks to these tests, first of all, the number of deaths in the population covered by the screening is reduced. Screening and early detection of the disease can also reduce the incidence of cancer. According to the recommendations, screening tests in Poland are performed to detect:
- breast cancer - mammography,
- cervical cancer - cytology,
- colorectal cancer - colonoscopy.
| All women between 25 and 59 years of age should undergo a pap smear test at least once every 3 years. Women over 50 should additionally participate in screening tests towards breast cancer and colorectal cancer:
|
You can read more about the above-mentioned tests, indications and preparation for their performance, as well as the course of the tests here >>
Men over 50 should be screened for prostate cancer and colorectal cancer:
|
Few women report for breast and cervical cancer screening in Poland. This is a serious health problem that requires a detailed analysis and revision of prevention recommendations. According to the data published by the National Health Fund, the implementation of population prevention programs is at a low level: 11.24% (cervical cytology) and 37.48% (breast mammography). times higher than that of the general population.
Medicover Prevention Standard
At Medicover, in addition to government preventive programs, we have been guided by the Medicover Prevention Standard in our daily practice for 10 years. It is a document describing Medicover's standard practices in the field of primary and secondary prevention, based on the current guidelines of Polish and foreign scientific societies and on the provisions of law in force in Poland. The scope of activities described in the Standard depends on the frequency of occurrence of particular conditions and diseases both in the general population and in the population of Medicover patients. Thus, it is a tool for implementing the postulates contained in the Medicover Quality Policy regarding the prevention and early detection of diseases.
The Medicover Prevention Standard is intended for people without symptoms of the disease for which the test is being performed, both for people who are not burdened with a family history of this disease.
Preventive actions carried out by a doctor or nurse/midwife include:
- interview and physical examination,
- measurements (weight, height, waist circumference),
- additional tests,
- vaccinations,
- preventive administration of drugs,
- lifestyle counseling.
The Medicover Prophylaxis Standard defines the scope of examinations for women and men of all ages. The final type and frequency of tests performed depends on the individual patient's health condition and risk factors.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR WOMEN:
- A control visit during which the doctor performs, among others:
- assessment of the skin, lips, mouth and throat, lymph nodes and thyroid,
- measurement of blood pressure, weight and height as well as waist circumference,
- calculation of body mass index (BMI),
- cardiovascular risk assessment according to SCORE,
- recommends performing examinations and vaccinations appropriate for age and health situation,
- Regular visits to the gynecologist,
- Regular cytology, breast ultrasound or mammography,
- Observation of moles on the skin,
- Regular dental check-ups,
- Preventive vitamin D supplementation,
- Breast self-examination.
Check how to properly examine your breasts? Download our material.
HOW TO EXAMINE THE BREASTS CORRECTLY?
- Examine your breasts while standing and lying down. Examine your breasts in the mirror. Any nipple asymmetry or skin change can be a warning sign.
- Raise your hand up behind your head, put your elbows back and again compare the symmetry and appearance of the breasts.
- Put your hands on your hips, push your shoulders and elbows forward. Again, carefully compare the symmetry and appearance of the breasts.
- In order not to miss any place, examine the breast point by point, drawing circular, vertical, horizontal or radial lines from the nipple.
- Raise your arm up. Carefully and slowly, with the tips of two or three fingers of the hand opposite to the breast being examined, press the nipple area and each of the four parts of the breast. Do the same with the other breast. By massaging around the nipple, check that there is no discharge from it.
- Examine the breast by palpation while lying down. Raise one arm high above your head, put a pillow or rolled up towel under your shoulder.
- Finally, check the axillary lymph nodes. Raise one hand to the level, and with the other explore the armpit.
Contact your doctor if you find:
- breast asymmetry;
- change in the appearance of the breast: redness, wrinkling, puffiness, skin sinking;
- nipple nodule: asymmetry, extension, ulceration, discharge;
- the appearance of changes that did not occur before.
RECOMMENDATIONS FOR MEN:
- A control visit during which the doctor performs, among others:
o assessment of the skin, lips, mouth and throat, lymph nodes and thyroid,
o measurement of blood pressure, weight and height as well as waist circumference,
o calculation of body mass index (BMI),
o cardiovascular risk assessment according to SCORE,
o recommends performing examinations and vaccinations appropriate for age and health situation,
- Regular PSA tests and tests for colorectal cancer,
- Observation of moles on the skin,
- Regular dental check-ups,
- Preventive vitamin D supplementation,
- Testicular self-examination.
Check how to properly test the testicles? Download our material.
How to properly test testicles?
- Examine your testicles once a month
- Examine your testicles during or after a warm shower
- Use the back of your hand to push your penis away
- Examine each testicle with both hands
- Slide the testicle between your fingers, applying gentle pressure
- Hold the top of the testicle with your thumb and support the bottom with your other fingers. Move your fingers relative to your thumb
It is normal that:
- The right testicle is slightly larger than the left
- You feel a thickening at the top of the testicle - this is the epididymis
- The epididymis may hurt a little when pressed
Contact your doctor if:
- You feel any thickening or lump on the surface of your testicle
- You will notice changes in testicle size
- You will notice soreness in the testicle when lightly touched
- You feel discomfort or pulling in your scrotum or groin.
In addition to the preventive recommendations contained in the European Code Against Cancer, it is worth paying attention to two more aspects that are obviously not associated with cancer. They are stress and sleep.
Stress
The relationship between the development of cancer and stress or the experience of traumatic situations, anxiety, depression was noticed already in the Middle Ages. Over the years, several concepts have emerged that try to explain this relationship. It was related, among others, with having type C personality, which is characterized by inhibition of feelings, withdrawal, denial of emotions, tendency to depression and pessimistic thinking.
Meanwhile, the mechanism of the relationship between stress and increased cancer incidence is pure biology. During stress, the hormones adrenaline and noradrenaline (so-called catecholamines) and cortisol (glucocorticoid) are secreted. The short-term effect of these compounds has a mobilizing character, is not harmful to health and does not have the power to cause cancer. In the case of prolonged tension and frustration, stress hormones, instead of supporting the body, have a destructive effect on it. Their effect is definitely longer and stronger than in a non-stressful situation. The higher the concentration of catecholamines, the more DNA damage and more cells undergoing neoplastic transformation. High concentrations of adrenaline and norepinephrine in the body cause vasoconstriction, which leads to their hypoxia and the development of new, subordinated to cancer cells. The consequence of this is the progression of the neoplastic disease and the increased risk of metastases.
In turn, cortisol contributes to the inhibition of the immune system and changes in the central nervous system. A properly functioning immune system searches the body, identifies pre-cancerous cells and eliminates them. However, if a person's immune defenses are weak, "rogue" cells that have gotten out of control of the body can multiply with impunity and form into cancer.
Uncontrolled stress also shortens telomeres (segments of DNA), which is another cause of shortening lifespan.
The epidemiological studies to date show that stress may be most strongly correlated with colorectal, breast, gastric and oesophageal cancer. In addition to being linked to cancer, stress also exacerbates asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Research also confirms that living in constant tension and pressure is associated with progressive impairment of cognitive functions - problems with memory, concentration, and association. It also increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases and intestinal problems.
The effects of long-term, chronic stress can be very extensive and affect both the psychological and somatic spheres. Changing our emotions for the better and greater control over them translates into better functioning of our entire body, which becomes stronger. Examples of methods of dealing with stress include visualization, relaxation techniques, mindfulness, breathing and stretching exercises.
We invite you to exercise together with our physiotherapist.
You can read more about sleep here: Stress | Symptoms, treatment, effects of stress (medicover.pl)
Dream
Healthy sleep is one of the basic factors affecting health. Although few of us attach importance to the importance of sleep for health and everyday functioning, scientific achievements of recent years prove that sleep plays an important role for our well-being, joy of life, success in learning and work, immunity of the body, and also for the risk of many diseases.
During sleep, many useful processes take place in the brain and throughout the body, such as:
- organizing and saving information, getting rid of unnecessary "garbage" from memory,
- reorganization and communication between nerve cells,
- rest and renewal of most tissues and organs of the whole body, as well as the production of useful amines and hormones.
Proper regeneration is therefore crucial for the proper functioning of our body. Lack of sleep negatively affects mental health. Sleep deprived people are more nervous and easily irritated, and also lack patience and succumb to stress faster. Lack of sleep also negatively affects mental clarity, memory and learning ability.
The evidence linking sleep to cancer is not very strong and this correlation requires further research. Nevertheless, there is strong scientific evidence that sleep deprivation is associated with weight gain, which is a risk factor for developing cancer. Other studies, on the other hand, show that people who sleep too little are more likely to develop type 2 diabetes. According to scientists, not getting enough sleep leads to a decrease in the sensitivity of tissues to insulin and, as a result, an increased risk of developing diabetes. One of the most important factors that increase the risk of developing, for example, endometrial cancer is diabetes. Constant sleep deprivation can also permanently damage the immune system, reduce the level of NK (Natural Killer) immune cells, responsible for the destruction of cancer and virus-infected cells, and cause symptoms of chronic inflammation.
It is recommended that an adult spend about 7-8 hours on night rest. Allow your body to regenerate. Take care of regular and good quality sleep.
Unfortunately, there are many factors that can interfere with a good night's sleep. These include, for example, bad habits, such as late meals, drinking alcohol or coffee, lack of exercise, or such simple matters as the wrong place and sleeping conditions (high temperature in the bedroom, uncomfortable bed), etc.
An important factor that may disturb sleep is also the excess of blue light emitted by computer or smartphone screens, which interferes with the secretion of melatonin. Medicover Optyk offers glasses that filter excess light of this length. Optometrists select the appropriate correction and provide tips on how to care for eye hygiene in the digital world.
- Video: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D80M8jjtSis
Another common cause of sleep disturbance is snoring. It has a huge impact on the quality of sleep, well-being during the day and health. It also disturbs the sleep of the snorer's family. It can also be a symptom of sleep apnea. Snoring and apnea need to be treated. Specialists from the MML ENT clinic help to get rid of these problems permanently.
- Learn more about how to get rid of snoring: https://niechrapanie.pl/
Changing your lifestyle protects you not only from cancer. The majority of scientific reports suggest that a proper lifestyle, including a proper diet and physical activity, avoiding smoking and maintaining a healthy body weight reduces the risk of developing type II diabetes by 93%, heart attack by 81% and stroke by 50% compared to people who did not follow any of the rules mentioned above.
Similar analyzes conducted in Norway or Spain show that failure to comply with the basic principles of cancer prevention, including the length of sleep or care for social well-being, shortens life by an average of 12-14 years.
Practicing all the recommendations mentioned above definitely determines our future in better health. It is worth taking responsibility for your own health today.
Implementation of appropriate preventive measures may translate into the following benefits for the population:
- improving health awareness and the health of the population,
- reduction of treatment costs,
- reducing the number of illnesses and deaths,
- reducing sickness absence, as well as the number of people with complications of diseases and permanent disability,
- increase in the percentage of cures,
- greater detection of diseases at an early stage of development
- lower financial losses (sickness benefits, production losses).
There is no 100% effective way to prevent cancer, but you can reduce your risk by making healthy choices, such as eating right, being physically active, avoiding drugs, and reducing stress. It's also important to follow recommendations for screening, which can help detect some cancers early. |
Take matters into your own hands! Design your health!




