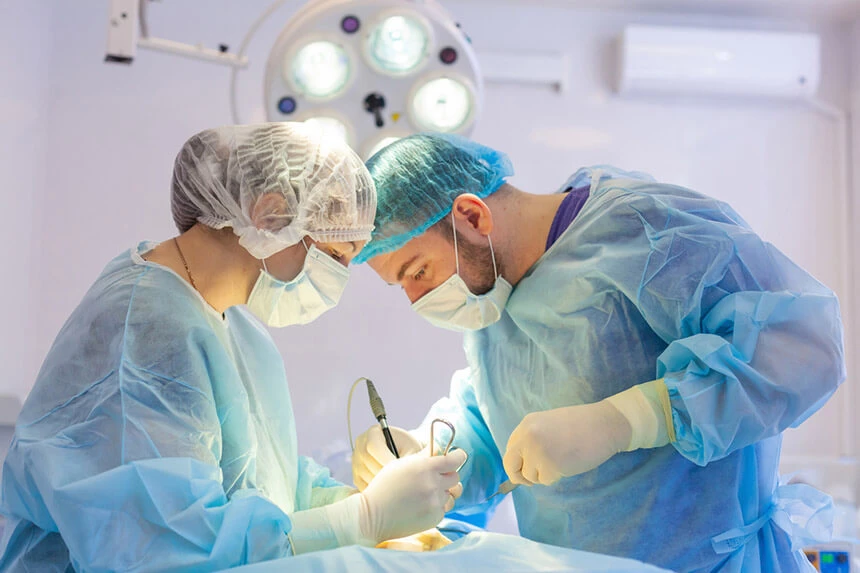
Cancer treatment in the 21st century is based on the concept of a comprehensive, interdisciplinary and holistic approach to cancer therapy. Thanks to new methods of treatment, in many cases it becomes a chronic disease, not a fatal disease. Modern oncology has a large arsenal of drugs and therapeutic procedures aimed at eliminating cancer cells. The latest reports on breakthrough therapies and ongoing clinical trials give patients hope to overcome the disease. The most common methods of cancer treatment are surgical treatment and chemotherapy. Since cancers can be systemic in nature, systemic treatment is a very common form of therapy.

Table of Contents:
Systemic treatment
This form of therapy involves the administration of systemic drugs.
The main methods of anticancer systemic treatment include:
- Chemotherapy – one of the most well-known methods of cancer treatment, which destroys cancer cells with drugs (cytostatics). The drugs administered may also affect healthy cells, causing certain side effects. Chemotherapy is used as a stand-alone method or as a treatment support – in combination with another method.
- Hormone therapy - is used in the case of hormone-dependent cancers. It involves the use of drugs that change the hormonal environment, which makes it possible to inhibit the growth of the cancer. There are two mechanisms of action of hormone therapy in oncological therapy. The first consists in limiting or eliminating their action, the second - in increasing the concentration of certain hormones.
- Immunotherapy - is an innovative method of cancer treatment. Its advantages are low invasiveness and acceptable toxicity. In this method, the immune system is used to fight cancer, stimulating its immune response against cancer. Most often, these are monoclonal antibodies directed against cancer antigens. to inhibit the development of cancer by blocking its growth factors.
- Targeted therapy – is a therapy in which drugs primarily target cancer cells and spare most normal cells. To apply it, it is necessary to identify the molecular profile of cancer cells and find differences between them and normal cells. A genetic analysis of the cancer cell is carried out, and then the molecular target, which is a change in its structure, is determined. This is how the drug is selected. It acts on a designated molecular target, which allows you to block specific receptors and inhibit the mechanisms of cancer cells. Targeted therapy is less toxic, so it causes fewer complications and side effects.
Intraperitoneal Hyperthermia Perfusion Chemotherapy (HIPEC)
It consists in administering a high dose of a cytostatic agent into the peritoneal cavity with a concentration much higher than is possible in the case of the intravenous route. Treatment with the HIPEC procedure consists in perfusion (flow, washing) of the peritoneal cavity with a fluid heated to 41-42°C with the simultaneous administration of an anticancer drug.

Surgical treatment
Surgical procedures are one of the basic methods of cancer treatment. Depending on the indications, surgery may be an element of combination therapy with other methods or the only indicated form of treatment. Due to the indications, we distinguish specific types of oncological surgical operations:
- Radical surgery – as a result, the cancer is completely removed from the patient's body.
- Cytoreductive surgery – performed to shrink or completely remove cancerous tissue prior to other surgical-associated treatment.
- Palliative surgery – used to increase the patient's comfort and general condition when there is no prospect of cure.
- Conserving operations – practiced in situations that do not require removal of the tumor with a margin that would qualify the procedure as radical.
- Reconstructive surgical procedures – allowing for the surgical reconstruction of removed tissues after radical surgical operations.
- Procedures performed to enable treatment with available methods - including if an intravascular port is implanted for administration, e.g. chemotherapy.
- Highly specialized treatments in cancer surgery - being part of combination therapy in such treatment methods as:
- intraperitoneal perfusion chemotherapy in hyperthermia (HIPEC - HyperthermicIntraPEritonealChemotherapy)
- Pressurized IntraPeritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC)
- Thermoablation
- Nano Knife, i.e. irreversible electroporation (IRE)
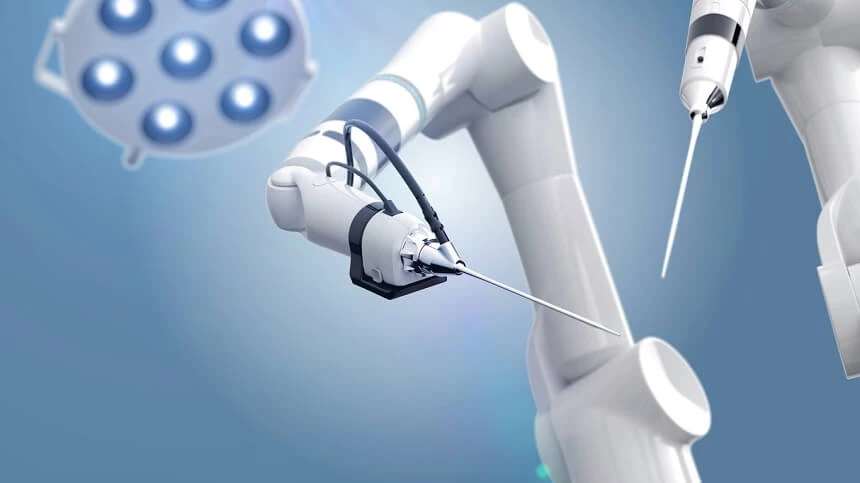
Robotic surgery
The development of medical technologies enables the use of robotic instruments in surgery. They allow to reduce the invasiveness and complications of surgical procedures. Procedures using robots are characterized by exceptional precision, which affects the effectiveness of the operation and reduces postoperative complications. Over the past 20 years, laparoscopic techniques have become the standard for many surgical procedures. Also noteworthy are the possibilities of using advanced devices, such as the Da Vinci robot.
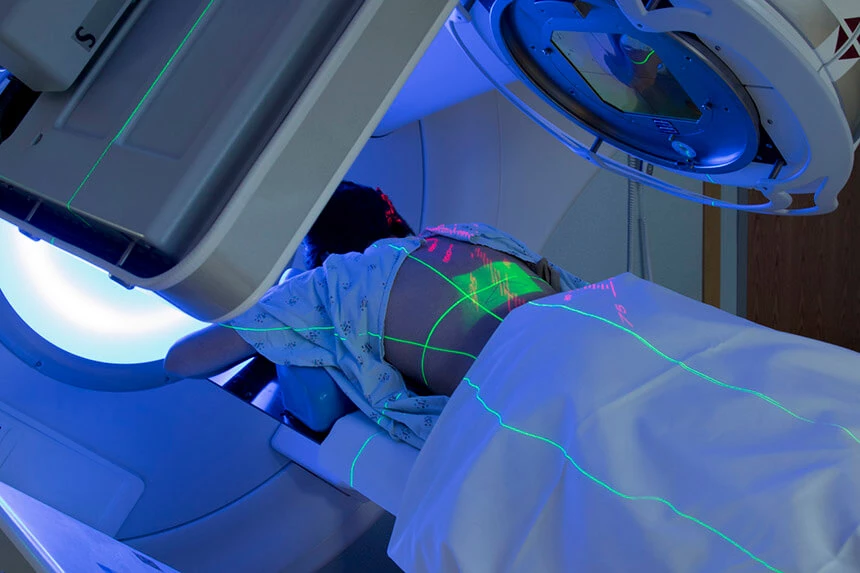
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a method of local treatment of cancer. It uses radiant energy for this purpose. Ionizing radiation directly affects DNA molecules, which leads to damage and ultimately to the death of cancer cells. Devices used in radiation therapy emit X-rays, gamma rays, electrons, alpha particles, neutron radiation. Due to the method of irradiation, we distinguish:
- teletherapy, in which the radiation source is placed at a certain distance from the tumor,
- brachytherapy, in which the radiation source is placed in close proximity to the tumour.
Nuclear medicine
Selected cancers can be treated with radioactive isotopes. This therapy consists in the emission of beta radiation, which destroys cancer cells, and only to a very small extent damages the healthy surrounding tissues.
Summary
| Taking into account the available methods of cancer treatment and the prospects brought by the development of medicine, oncological patients today have a good chance for the success of their therapeutic process. Recognition of the type, characteristics and stage of the tumor allows to adjust the therapy to a specific case. Depending on the patient's health condition and the stage of the therapeutic process, various treatment methods can be used simultaneously, which increases the chance of recovery. In the selection of therapy, not only effectiveness is important, but also the likelihood of complications and side effects determining the comfort and quality of life of oncology patients. |